- 1. Answer the following questions about the structure (right).
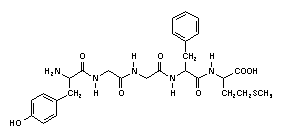
- a. Structural classification = PENTAPEPTIDE
- b. Physiological function = ENKEPHALINERGIC NEUROTRANSMITTER
- c. Acid-base character = AMPHOTERIC (ACIDIC AND BASIC)
- b. Physiological function = ENKEPHALINERGIC NEUROTRANSMITTER
- 2. Answer the following questions about the structure below.
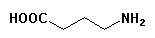
- a. Structural classification = AMINO MONOACID
- b. Physiological function = INHIBITORY NEUROTRANSMITTER
- c. Acid-base character = Both acidic and basic (amphoteric)
- d. Metabolite of this structure = HOOC(CH2)2CHO ()
- b. Physiological function = INHIBITORY NEUROTRANSMITTER
- 3. Answer the following questions about the drug structure
- a. Possible therapeutic use of drug a: NARCOTIC ANALGESIC
- b. Possible therapeutic use of drug b: NARCOTIC ANTAGONIST
- c. Drug a has a pKa of 8.0 while drug b has a pKa of 6.75. Which drug will likely have the most rapid onset of action. Explain why.
The less basic drug, b, will have higher CNS bioavailability because of lesser ionization at physiologic pH.
- 4. Answer the questions about the following drug structures (A, B, C and D)
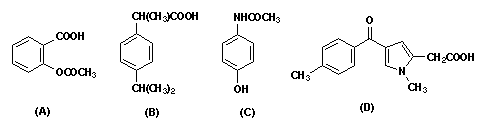
- a. Match these drugs with the correct structural class (place letter on line).
A = Salicylate, B = Profen, C = Anilide, D = Arylacetic acid
- b. List those drugs, by letter, that have a pKa that is less than 7.4.
A, B, D (all are COOH derivatives)
- c. List those drugs, by letter, that have therapeutically-useful antiinflammatory actions.
A, B, D (all are COOH derivatives)
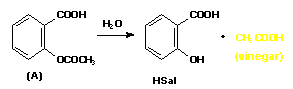
- d. Dosage forms containing drug A are subject to chemical decomposition detectable by a "vinegary odor". Show the chemical reaction likely involved in this decomposition.
- e. Drug B is formulated as the racemate but only the S-isomer possesses the desired pharmacologic activity. Why is the drug not formulated as the single, bioactive isomer?
Human metabolism utilizes a racemase to convert some of the R–enantiomer supplied by the racemate to the bioactive S–isomer rather than vice versa.
- f. Show the metabolic transformations involved in production of hepatic toxicity by drug C.
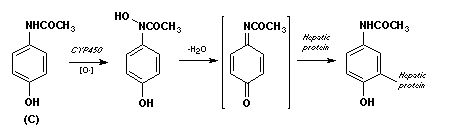
- g. Show the metabolic reaction responsible for terminating the pharmacologic activity of drug D.
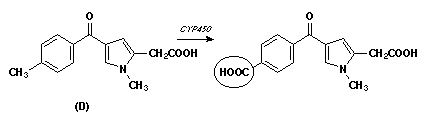
You can download a WordPerfect 6.1 (quiz2.wpd) file of this page by clicking here!
Click here to return to: PY420 Home Page
- a. Possible therapeutic use of drug a: NARCOTIC ANALGESIC